A Guide to Eco-Friendly Food Choices
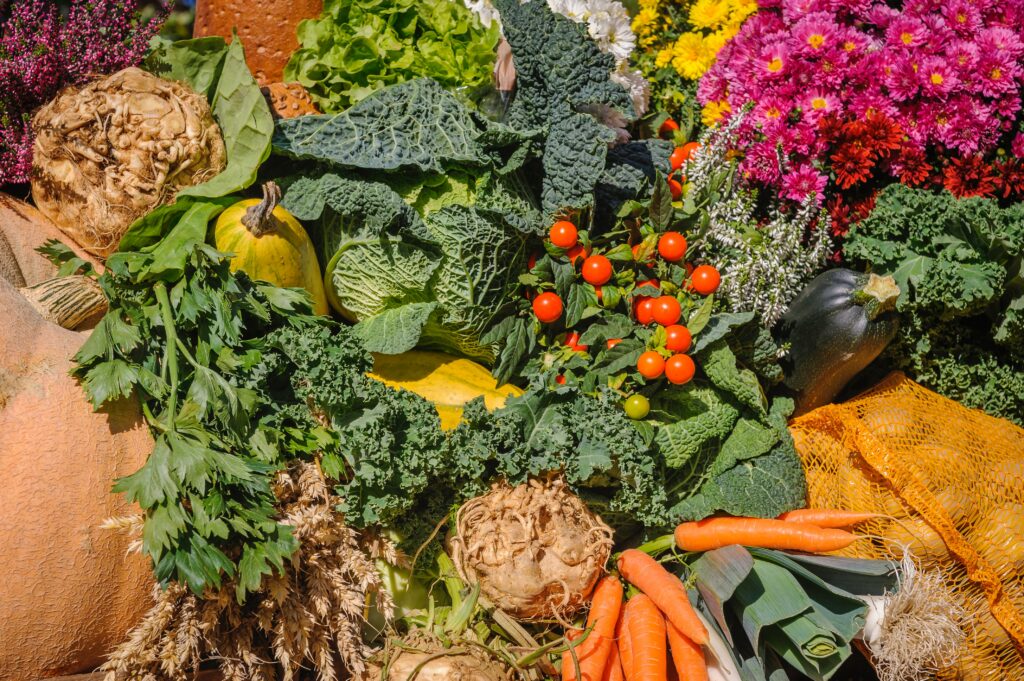
Seasonal eating is a simple yet impactful concept revolving around choosing fruits and vegetables that are naturally harvested in the current season. It is grounded in the tradition of eating what the earth produces at a given time, but today, it’s gaining attention for its role in sustainability. This approach to consumption not only promises fresher, tastier produce but also boasts significant environmental benefits. By aligning our diets with the natural growing cycles, food travels shorter distances from farm to table, resulting in lower carbon emissions and reduced need for storage and transportation.
One of the key environmental benefits of seasonal eating is the support it lends to local farming communities and ecosystems. When consumers opt for seasonal foods, they are often purchasing directly from nearby growers, which bolsters the local economy and reduces the reliance on imports. Additionally, seasonal produce typically requires fewer chemical interventions, as it is grown during its natural growing season, thus minimizing the impact of pesticides and fertilizers on the environment. Embracing the variety offered by each season can lead to a more diverse diet, one that not only enhances personal health but also the health of the planet.
Moreover, seasonal eating encourages a harmonious relationship with nature’s cycles. Eating seasonally means foods are often grown in optimal conditions, enhancing their nutritional content. For instance, strawberries in summer or squashes in fall are not only at their peak of flavor but are also packed with nutrients. This natural rhythm further allows for the soil to rest and replenish between crops instead of being forced to produce the same fruit or vegetables all year round. By adopting a seasonal diet, people are contributing to reduced water stress and a decrease in land use change, ultimately promoting biodiversity and environmental sustainability.
The Science of Seasonal Eating
Seasonal eating explores how consuming fruits and vegetables during their natural growing season can lead to better nutrition and a more sustainable lifestyle. This approach not only supports local agriculture but also promotes a reduced carbon footprint due to less transportation.
Nutritional Advantages of Seasonal Produce
Seasonal produce is known for being rich in vitamins and minerals. For instance, strawberries and tomatoes harvested at their peak season have heightened levels of antioxidants and flavor. Nutritionally, eating what is grown locally and seasonally ensures that fruits and vegetables are consumed when their nutritional value is highest.
Agricultural and Environmental Impacts
Agriculture that focuses on seasonal crops typically requires less energy and emissions. As seasonal produce thrives in its natural environment, it usually needs fewer interventions, reducing the overall carbon footprint and mitigating climate change.
Economic and Social Considerations
Eating seasonally bolsters the local economy by supporting farmers markets and community-supported agriculture. People who buy seasonally are often motivated by a desire to strengthen their local food systems and to ensure farmers receive a fair sale for their produce.
Seasonal Food Through the Year
Different seasons bring different crops. In spring, asparagus sprouts; summer yields a bounty like tomatoes; fall is rich with pumpkin and winter squash; while winter offers storage-friendly crops such as apples and pears. These items embody the essence and flavors of their respective seasons.
Understanding Food Miles and Transportation
The concept of food miles refers to the distance food travels from production to consumer, often involving transportation by plane or truck. Locally grown, seasonal food tends to travel fewer miles, thus reducing associated pollution and environmental impact.
Culinary Benefits and Preservation
Culinary experts often cite the superior taste and flavor of fresh, seasonal produce. Chefs and home cooks alike value the variety of seasonality, which also lends itself well to preserving techniques to extend the enjoyment of seasonal bounty throughout the year.
Health and Dietary Benefits
Incorporating seasonal fruits and vegetables into one’s diet can enhance overall health. For example, winter squash is a great source of essential vitamins and minerals, while a diverse range of produce throughout the year can support a balanced diet with an array of health benefits.
Choosing and Supporting Seasonal Eating
In the pursuit of a more sustainable lifestyle, one critical area to focus on is our food choices. Specifically, the shift towards seasonal eating brings about significant advantages for both the individual and the planet. This section delves into how one can identify seasonal foods, their benefits to the local community, ways they can reduce environmental impact, and practical tips for incorporating seasonal produce into daily meals.
Identifying Seasonal Foods
To begin with, identifying what’s in season can be as simple as visiting local farmers markets or checking with local grocery stores, which often highlight seasonal produce. These places are treasure troves of the freshest fruits like oranges and vegetables such as lettuce and broccoli, signalling their optimal harvest time. Many websites and apps related to the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs also provide calendars detailing peak seasons for various produce types.
Benefits for the Local Community
Supporting seasonal eating significantly bolsters the local economy. When consumers choose locally grown food, they are directly contributing to the livelihood of local farmers. Participating in community-supported agriculture (CSA) further ensures that the money spent stays within the community and encourages the growth of local food markets.
Reducing Environmental Impact
Opting for seasonal foods also means a reduction in energy use associated with storage and transportation, ultimately leading to a lower environmental impact. Foods that don’t need to be shipped from afar help reduce pollution and food waste, while preserving natural resources and biodiversity, contributing to a sustainable diet that benefits both the planet and society.
Seasonal Eating Tips and Tricks
Here are some straightforward tips to make seasonal eating an effortless part of life:
- Plan your meals around the seasonal produce available in your area.
- Be flexible with recipes, substituting ingredients with what’s available and fresh.
- Preserving techniques like canning or freezing can prolong the taste and nutritional value of seasonal produce.
- Educate yourself on how long fresh produce can be stored and the best methods to maintain its quality.
Through these practices, choosing and supporting seasonal eating is not just a beneficial choice—it becomes a simple and deeply rewarding one.